This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
proofread
Insights from a comprehensive vehicle lifecycle study for carbon reduction in transportation
Transportation is the third largest contributor to global carbon emissions. Addressing this issue is important for countries worldwide. High-speed railways (HSR) are considered the main direction for the future of intercity transportation due to their high degree of electrification. However, there has been a lack of relevant data to support how much carbon reduction high-speed rail travel can bring about and the most effective regulatory approaches for various transportation modes.
To that end, in a recent study published in the journal High speed Railway, researchers from Beijing Jiaotong University analyzed the entire life cycle carbon emissions of vehicles.
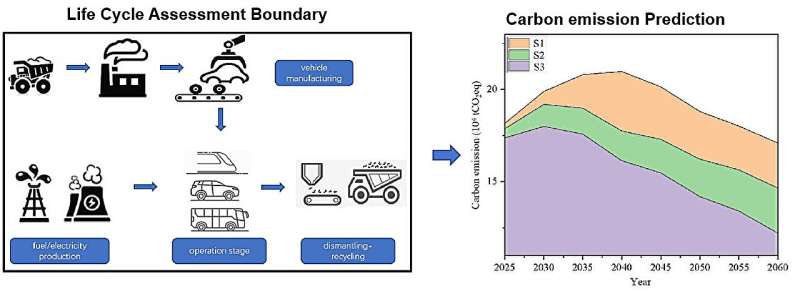
"The entire life cycle reflects the complete process of a product or tool, from natural resources use to its eventual return to nature. This mirrors the entire life process of human beings," explains the study's lead author, Lu Yintao, an associate professor at the School of Environment at Beijing Jiaotong University. "Assessing carbon emissions throughout the entire life cycle provides a more accurate gauge of a product's environmental friendliness."
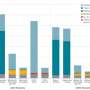
Historically, road transportation has been the main mode of passenger travel, including private cars, buses and railways, with each using multiple energy sources such as gasoline and electricity. This study considers these factors and adopts a per-person-per-kilometer evaluation unit to inform which transportation combinations are more effective in reducing carbon emissions during travel.
Currently, many studies on carbon reduction in transportation vehicles focus on the full lifecycle carbon emission accounting of infrastructure. In contrast, this study was conducted based on the perspective of the full life cycle of vehicles and fuels.
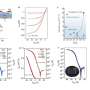
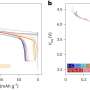
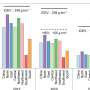
"Notably, when compared to infrastructure, vehicles are more consumable, whereas HSR demonstrates significant carbon emission reduction, with an intensity of only 24%–32% compared to private vehicles and 47%–89% compared to buses," shares Lu.
The study not only contributes to carbon reduction in transportation but also provides information for vehicle manufacturers regarding the materials they should prioritize for production, given their significant carbon reduction implications.
Yao Hong, senior author of the study, believes that carbon emissions during transportation are a continuous process and play an important role in the entire life cycle of carbon emissions. She hopes that this research can provide theoretical support for China's carbon reduction efforts in the transportation sector.
More information: Yintao Lu et al, Carbon emissions reduction potentiality for railroad transportation based on life cycle assessment, High-speed Railway (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.hspr.2023.08.004