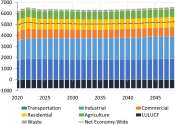
EPA says its new strict power plant rules will pass legal tests
The EPA on Thursday announced a series of actions to address pollution from fossil fuel power generators, including a final rule for existing coal-fired and new natural gas-fired plants that will eventually require them to ...
Apr 25, 2024
0
1