This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Imaging grain boundaries that impede lithium-ion migration in solid-state batteries
A NIMS research team has developed a new technique to image grain boundaries obstructing lithium-ion migration in solid-state batteries—a promising type of next-generation battery.
Solid-state batteries—next-generation rechargeable batteries—are intended to be safer and have higher energy densities than conventional lithium-ion batteries by replacing liquid organic electrolytes with solid electrolytes. A major issue in current solid-state battery R&D is the obstruction of lithium-ion migration at the interfaces between active materials and solid electrolytes and at the grain boundaries within solid electrolytes.
These obstructions lower charge/discharge rates and reduce energy density in batteries. A solid electrolyte is composed of crystalline grains and the boundaries between them. Existing ionic conductivity evaluation methods had only been able to measure average ionic conductivity across a solid electrolyte and were unable to quantify ionic conductivity at individual grain boundaries and identify boundaries restricting ionic migration.
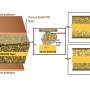
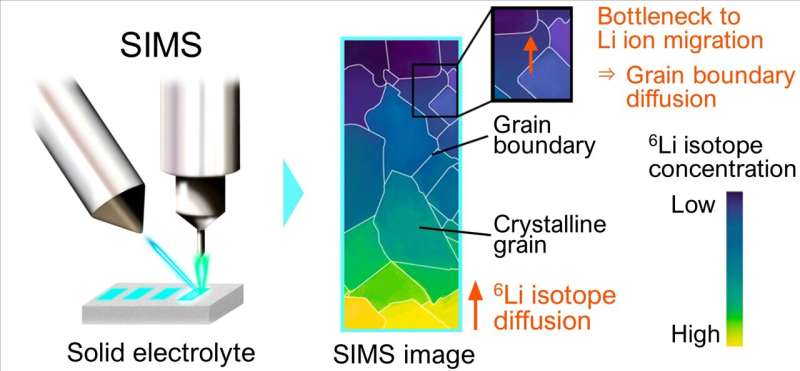
This research team succeeded in imaging and quantifying ionic migration/diffusion at individual grain boundaries within a solid electrolyte using secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS). SIMS enables the imaging of chemical element distribution across a solid electrolyte specimen by sputtering the surface of the specimen with a focused primary ion beam and collecting and analyzing ejected secondary ions.
The team first replaced a portion of a stable lithium isotope, 7Li (mass number: 7, natural abundance: 92%), constituting an electrolyte specimen with another lithium isotope, 6Li (mass number: 6, natural abundance: 8%), at the edge of the specimen using an isotope exchange technique.
The team then observed the diffusion of 6Li within the specimen using SIMS. Because it was impossible to image and quantify the distribution of fast-diffusing 6Li using conventional SIMS, the team significantly slowed 6Li diffusion by cooling the specimen (i.e., cryo-SIMS), enabling the team to precisely measure the 6Li distribution and identify grain boundaries acting as bottlenecks to ionic migration.
The cryo-SIMS technique can be used to directly observe lithium-ion diffusion, identify interfaces/grain boundaries acting as bottlenecks among the many interfaces/boundaries existing in a solid-state battery, and determine the causes of these obstructions. This approach is expected to contribute to the development of higher-performance solid-state batteries.
The work is published in the Journal of Materials Chemistry A.
More information: Gen Hasegawa et al, Visualization and evaluation of lithium diffusion at grain boundaries in Li0.29La0.57TiO3 solid electrolytes using secondary ion mass spectrometry, Journal of Materials Chemistry A (2023). DOI: 10.1039/D3TA05012B