This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Off-road autonomous driving tools focused on camera vision

Southwest Research Institute has developed off-road autonomous driving tools with a focus on stealth for the military and agility for space and agriculture clients. The vision-based system pairs stereo cameras with novel algorithms, eliminating the need for lidar and active sensors.
"We reflected on the toughest machine vision challenges and then focused on achieving dense, robust modeling for off-road navigation," said Abe Garza, a research engineer in SwRI's Intelligent Systems Division.
Through internal research, SwRI engineers developed a suite of tools known as the Vision for Off-road Autonomy (VORA). The passive system can perceive objects, model environments, and simultaneously localize and map while navigating off-road environments.
The VORA team envisioned a camera system as a passive sensing alternative to lidar, a light detection and ranging sensor that emits active lasers to probe objects and calculate depth and distance. Though highly reliable, lidar sensors produce light that hostile forces can detect. Radar, which emits radio waves, is also detectable. GPS navigation can be jammed, and its signals are often blocked in canyons and mountains, which can limit agricultural automation.
"For our defense clients, we wanted to develop better passive sensing capabilities but discovered that these new computer vision tools could benefit agriculture and space research," said Meera Towler, a SwRI assistant program manager who led the project.
The researchers developed the VORA technology to explore planetary surfaces. In space applications, autonomous robots are limited by power, payload capacity, and intermittent connectivity. In space, cameras make more sense than power-hungry lidar systems.
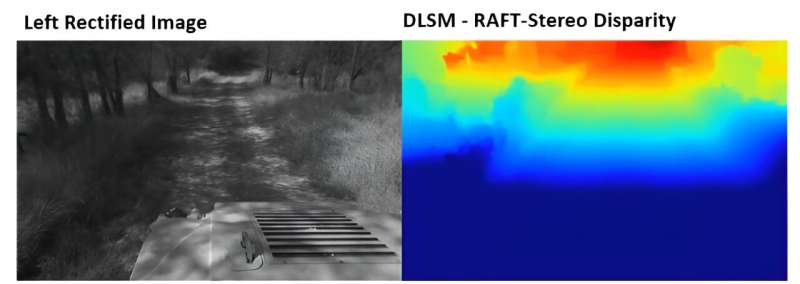
To overcome various challenges, the team developed new software to use stereo camera data for high-precision tasks traditionally accomplished by using lidar. These tasks include localization, perception, mapping, and world modeling.
Based on this research, SwRI developed a deep learning stereo matcher (DLSM) tool, which uses a recurrent neural network to create dense, accurate disparity maps from stereo vision. A disparity map highlights motion differences between two stereo images.
To aid in simultaneous localization and mapping, SwRI developed a factor graph algorithm to intelligently combine sparse data from stereo image features, landmarks, inertial measurement unit (IMU) readings, and wheel encoders to produce highly accurate localization data. Autonomous systems use factor graphs, or probabilistic graphical models, to make inferences by comparing variables.
"We apply our autonomy research to military and commercial vehicles, agriculture applications, and so much more," Towler said. "We are excited to show our clients a plug-and-play stereo camera solution integrated into an industry-leading autonomy stack."
SwRI plans to integrate VORA technology into other autonomy systems and test it on an off-road course at SwRI's San Antonio campus.
SwRI has made safety and security a priority in the development of autonomous vehicles and automated driving systems as the technology reaches advanced levels of readiness for commercial and governmental use.
More information: Project homepage: www.swri.org/industries/autono … cle-research-testing