This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
proofread
Understanding the impact of environmental factors on molded fiber products
Since 2020, the annual market size of molded fiber product (MFP) worldwide has exceeded $3.5 billion US, and is growing rapidly. The reliability of MFP is closely related to its mechanical properties during the use. The unpredictable mechanical properties make it difficult to design and improve MFP.
In a study published in the Journal of Bioresources and Bioproducts, a group of researchers from China has outlined some mathematical models of the mechanical parameters of MFP they constructed. The change of mechanical parameters of MFP with moisture content (MC) was described, and the change of MC with temperature and humidity was described by the moisture sorption isotherm.
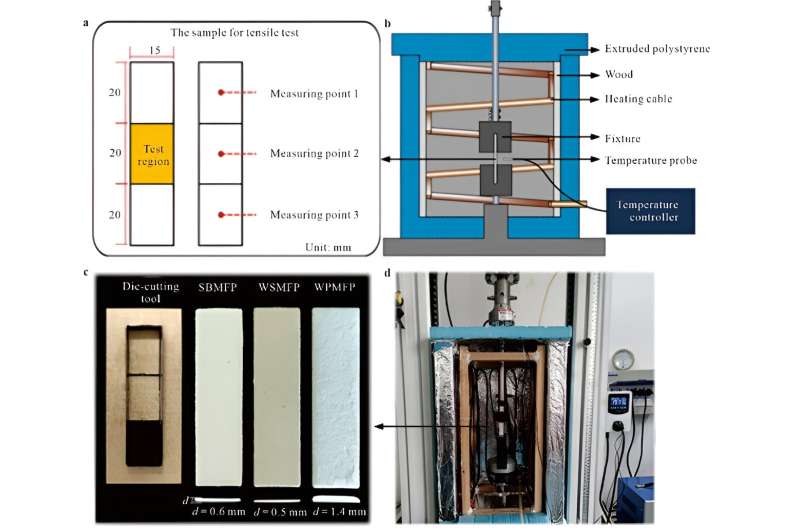
"The preparation of MFP often requires the first preparation of the mold, but the time and labor cost of repeatedly preparing the mold verification are too high. These costs can be greatly reduced by the method of numerical simulation, and the mechanical parameters of the material are essential in the numerical simulation process," explains one of the study's authors, Zhiqiang Fu, lecturer in light industry technology and engineering for School of Light Industry Science and Engineering at Tianjin University of Science and Technology.
"The constructed functions of mechanical parameters with the change of environment can provide support for the structural design and improvement of MFP under different working conditions. The mechanical properties of MFP are directly affected by MC, and the MC was affected by ambient temperature and humidity. However, the temperature also affects the molecular activity, which directly affects the mechanical properties of the MFP."
The study's team found that the direct effect of temperature (20−70°C) on mechanical properties of MFP was insignificant, and the mechanical properties of MFP were mainly changed by MC. The MC was related to ambient temperature and humidity, and the relationship between the three could be described by the modified Guggenheim-Anderson-de Boer (GAB) model (20−70°C and 30%−90% relative humidity).
With the increase of MC, the elastic modulus and fracture strain was increased and decreased linearly, the yield strength and failure strength were presented GaussAmp laws, and the failure strain was presented asymptotic regressed distribution law.
According to Fu, the investigator who led the study, "This is of great significance for understanding the effects of temperature, humidity and MC on the mechanical properties of MFP. In previous studies, temperature and MC changes often occur simultaneously, so it is difficult to understand the main way in which temperature affects the mechanical properties of MFP. We hope that our results will help people understand the effects of temperature, humidity and MC on MFP, and provide help for the engineering application of MFP."
More information: Zhiqiang Fu et al, Study on the mechanism and law of temperature, humidity and moisture content on the mechanical properties of molded fiber products, Journal of Bioresources and Bioproducts (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.jobab.2024.04.003