This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
proofread
Offline/online attribute-based searchable encryption scheme from ideal lattices
The security of traditional attribute-based searchable encryption schemes relies on traditional number-theoretic assumptions, and thus they are not able to resist the threat of quantum algorithms. Existing lattice-based searchable encryption schemes have two main problems: one is the low efficiency of the execution of encryption, key generation and search algorithms. The second is the large space required for storing search trapdoors.
To solve the problems, a research team led by Yang Yang conducted new research and published their findings in Frontiers of Computer Science.
The team proposes an offline/online attribute-based searchable encryption scheme from ideal lattices (ABSEIL). Benefiting from the keyword search function of ABSEIL scheme, authorized consumers can efficiently retrieve the desired data with a lightweight search trapdoor.
Through online/offline technology, complex arithmetic operations in encryption and key generation algorithms are pre-executed in the offline phase, and the online phase only involves a few arithmetic operations. Additionally, ABSEIL scheme incorporates the proxy re-encryption mechanism for completing end-to-end data sharing.
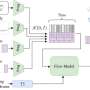
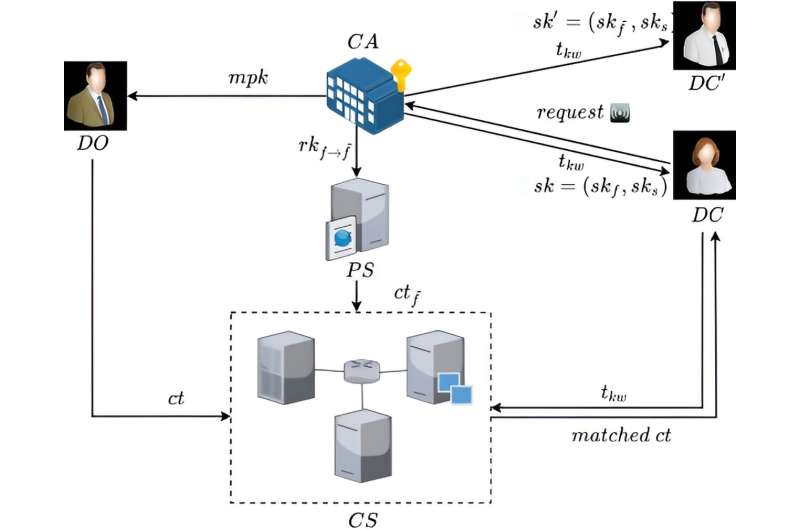
ABSEIL involves five types of participants: central authority (CA), data owner (DO), data consumer (DC), proxy server (PS) and cloud server (CS).
CA plays the role of initializing the system. Then it generates the master public key for all entities together with the master secret key for itself. Also, it grants secret key to all data consumers. DO encrypts data, and uploads the ciphertext to CS. Before decrypting, DC requests a searchable trapdoor from CA and forwards it to CS to search for matched.
DC can initiate a request to CA to produce a re-encryption key. Then CA transfers to PS. In this setting, DC delegates the decryption right to the through the authorization of CA. PS utilizes to produce a fresh re-encrypted ciphertext, then transfers to CS. CS supplies storage services. Furthermore, CS utilizes to search for matched ciphertext for DC.
More information: Yang Yang et al, Offline/online attribute-based searchable encryption scheme from ideal lattices for IoT, Frontiers of Computer Science (2024). DOI: 10.1007/s11704-023-3128-3