This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Defect passivation strategy improves perovskite solar cell efficiency

Solar energy is a promising way of reducing our dependence on fossil-fuel-based energy resources to opt for cleaner energy forms. Over the years, solar cells that can harness this renewable energy have undergone significant progress.
Metal-halide perovskite has gained significant attention as a promising light-absorbing material for solar cells due to their exceptional optoelectronic properties which enable them to efficiently generate energy from sunlight.
A popular choice of material for building high power conversion efficiency (PCE) perovskite solar cells (PSCs) is polycrystalline formamidinium lead iodide (FAPbI3) owing to its narrow energy band gap. Despite their superior optoelectronic properties and versatility, polycrystalline perovskites like FAPbI3 often suffer from defects (imperfections) in their crystal structure which are harmful to the structural stability and carrier dynamics, ultimately affecting their energy conversion abilities.
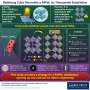
To fill this gap, a team of researchers led by Professor Hobeom Kim from the Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST) has developed a new defect passivation strategy, a process to significantly reduce defects and improve PCE and stability of perovskite solar cells.
In their recent study published on July 4, 2024 in Nature Communications, the team reported introducing hexagonal polytype (6H) [different structural forms with the same composition] perovskite into the cubic polytype (3C) FAPbI3, which led to a remarkable increase in their PCE when compared to their counterparts.
But why use 6H perovskite polytype? "A typical approach so far has been to introduce an external chemical reagent to deal with the defect problem. However, bringing in external reagents could directly impact the crystalline quality of the perovskite during crystal growth, so our work does not rely on such stabilizers. Instead, we employ a chemically identical polytype of perovskite, 6H polytype containing a corner-sharing component that effectively suppresses the formation of defects in perovskite," explains Prof. Kim.
The researchers incorporated 6H perovskite into FAPbI3, by using excess of lead iodide and methylammonium chloride, thereby creating a component that intervened with the dominant defect site (halide vacancies, VI+) of α-phase cubic polytype (3C) FAPbI3.
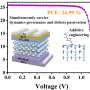
They found that the 6H phase improved the structural integrity and carrier dynamics of FAPbI3. This led to an ultralong carrier lifetime of greater than 18 microseconds, PSCs with PCEs of 24.13% and a module with PCEs of 21.92% (certified power conversion efficiency of 21.44%) with long-term operational stability.
The researchers suggested that the 3C/6H hetero-polytypic perovskite design might be the closest to the ideal configuration of a polycrystalline perovskite film. The study demonstrated how engineering defects in perovskite can accelerate the development of advanced PSCs for personal and commercial uses, such as in rooftop solar panels, wearable electronics, and portable chargers.
"Perovskite solar cells offer a transformative solution for achieving carbon neutrality and addressing global warming. Their efficiency, versatility, and reduced environmental impact make them an essential component in the transition to a sustainable future," concludes Prof. Kim.
More information: Hobeom Kim et al, Shallow-level defect passivation by 6H perovskite polytype for highly efficient and stable perovskite solar cells, Nature Communications (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-50016-6