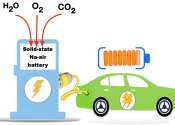
Researchers develop high-energy, high-efficiency all-solid-state sodium-air battery
A research team has successfully developed a high-energy, high-efficiency all-solid-state sodium-air battery. This battery can reversibly utilize sodium (Na) and air without requiring special equipment. The team was led by ...
May 28, 2024
0
93