Soft e-skin that communicates with the brain
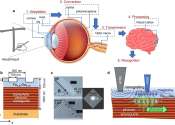
Researchers at Stanford University have developed digital skin that can convert sensations such as heat and pressure to electrical signals that can be read by electrodes implanted in the human brain.
Robotics

Researchers at Stanford University have developed digital skin that can convert sensations such as heat and pressure to electrical signals that can be read by electrodes implanted in the human brain.
Engineering

Artificial intelligence (AI) plays an important role in many systems, from predictive text to medical diagnoses. Inspired by the human brain, many AI systems are implemented based on artificial neural networks, where electrical ...
Jun 7, 2022
0
487
Computer Sciences

With a simple artificial nervous system now able to mimic human responses to light, scientists are learning more about how to program such technology for use in medical robotic prostheses.
Engineering

Combining new classes of nanomembrane electrodes with flexible electronics and a deep learning algorithm could help disabled people wirelessly control an electric wheelchair, interact with a computer or operate a small robotic ...
Sep 20, 2019
0
1239
Engineering

Researchers commonly study brain function by monitoring two types of electromagnetism—electric fields and light. However, most methods for measuring these phenomena in the brain are very invasive.
Oct 22, 2018
0
133
Robotics

Getting robots to do things isn't easy: usually scientists have to either explicitly program them or get them to understand how humans communicate via language.
Jun 20, 2018
0
355
Hi Tech & Innovation

Imagine playing a racing game like Mario Kart, using only your brain to execute the complex series of turns in a lap.
Mar 29, 2024
0
197
Hardware
In the future, modern machines should not only follow algorithms quickly and precisely, but also function intelligently—in other words, in a way that resembles the human brain. Scientists from Dortmund, Loughborough, Kiev ...
Feb 7, 2024
0
160
Hi Tech & Innovation

In a world-first, researchers from the GrapheneX-UTS Human-centric Artificial Intelligence Centre at the University of Technology Sydney (UTS) have developed a portable, non-invasive system that can decode silent thoughts ...
Dec 11, 2023
0
388
Machine learning & AI
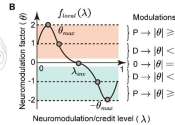
Catastrophic forgetting, an innate issue with backpropagation learning algorithms, is a challenging problem in artificial and spiking neural network (ANN and SNN) research.
Sep 1, 2023
0
107