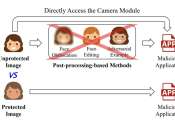
A camera-based anti-facial recognition technique
Facial recognition systems, computational tools that can recognize individuals in images or video footage, are now widely employed worldwide. Some users and developers, however, have raised privacy-related concerns, as by ...