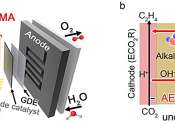
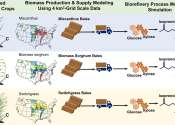
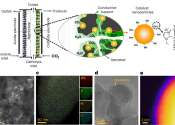
The carbon cycle is the biogeochemical cycle by which carbon is exchanged among the biosphere, pedosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere of the Earth.
The carbon cycle is usually thought of as four major reservoirs of carbon interconnected by pathways of exchange. These reservoirs are:
The annual movements of carbon, the carbon exchanges between reservoirs, occur because of various chemical, physical, geological, and biological processes. The ocean contains the largest active pool of carbon near the surface of the Earth, but the deep ocean part of this pool does not rapidly exchange with the atmosphere.
The global carbon budget is the balance of the exchanges (incomes and losses) of carbon between the carbon reservoirs or between one specific loop (e.g., atmosphere ↔ biosphere) of the carbon cycle. An examination of the carbon budget of a pool or reservoir can provide information about whether the pool or reservoir is functioning as a source or sink for carbon dioxide.