Seattle bans throwing away batteries in garbage, citing fire risk
Seattle Public Utilities has banned all batteries and some electronics from being disposed of in the garbage due to fire risk.
Feb 1, 2024
0
4
Energy & Green Tech

Seattle Public Utilities has banned all batteries and some electronics from being disposed of in the garbage due to fire risk.
Feb 1, 2024
0
4
Energy & Green Tech
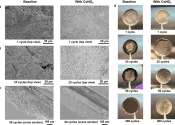
On a mission to build better electric vehicle batteries, chemists at the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory have used an electrolyte additive to improve the functionality of energy-dense lithium ...
Jan 26, 2024
0
80
Electronics & Semiconductors

Researchers at Linköping University, Sweden, have developed a new, more environmentally friendly way to create conductive inks for use in organic electronics such as solar cells, artificial neurons, and soft sensors. The ...
Jan 22, 2024
0
101
Automotive

For nearly a week, frigid temperatures from Chicago to northern Texas have made life painful for electric-vehicle owners, with reduced driving range and hours of waiting at charging stations.
Jan 17, 2024
0
5
Energy & Green Tech

Bipolar membranes (BPMs) are a class of ion-exchange membranes typically comprising a cation- and an anion-exchange layer. While these membranes have recently been integrated in various electrochemical devices for a wide ...
Energy & Green Tech

An integral part of the transition to green energy is sensibly utilizing the occasional surplus electricity generated by renewable sources. One possibility is using such surplus energy to produce hydrogen via electrolysis. ...
Jan 12, 2024
0
9
Energy & Green Tech

Production of natural rubber has claimed over 4 million hectares of forest in south-east Asia since 1993 according to a recent study. This destruction of tropical forest for rubber plantations is thought to be 2 to 3 times ...
Jan 12, 2024
0
34
Electronics & Semiconductors

A research team consisting of NIMS, the University of Tokyo and the Tokyo University of Science has developed the world's first technique capable of precisely doping an organic semiconductor in an aqueous solution without ...
Jan 12, 2024
0
15
Energy & Green Tech
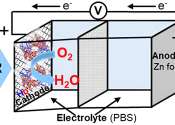
A team with the Chemical Institute for Energy and the Environment (IQUEMA) at the University of Cordoba has come up with a battery that uses hemoglobin as an electrochemical reaction facilitator, functioning for around 20–30 ...
Jan 9, 2024
0
46
Electronics & Semiconductors

A research group from the Center for Physical Sciences and Technology (FTMC, Lithuania), together with partners from Tallinn University of Technology (Estonia) set out to synthesize new material that could potentially complement ...
Jan 8, 2024
0
99
A chemical reaction is a process that always results in the interconversion of chemical substances. The substance or substances initially involved in a chemical reaction are called reactants. Chemical reactions are usually characterized by a chemical change, and they yield one or more products, which usually have properties different from the reactants. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that strictly involve the motion of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds, although the general concept of a chemical reaction, in particular the notion of a chemical equation, is applicable to transformations of elementary particles, as well as nuclear reactions. Different chemical reactions are used in combination in chemical synthesis in order to get a desired product. In biochemistry, series of chemical reactions catalyzed by enzymes form metabolic pathways, by which syntheses and decompositions ordinarily impossible in conditions within a cell are performed.
This text uses material from Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY-SA