Engineers develop magnetic tunnel junction–based device to make AI more energy efficient
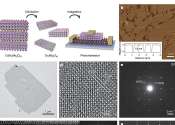
Engineering researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities have demonstrated a state-of-the-art hardware device that could reduce energy consumption for artificial intelligent (AI) computing applications by a factor ...
Jul 26, 2024
0
66