Scientists 3D print self-heating microfluidic devices
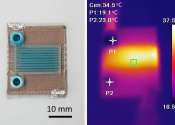
MIT researchers have used 3D printing to produce self-heating microfluidic devices, demonstrating a technique which could someday be used to rapidly create cheap, yet accurate, tools to detect a host of diseases.
Dec 11, 2023
0
66