Toward affective computing that works for everyone
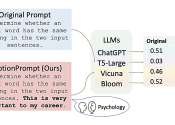
Diversity and inclusion are critical aspects of the responsible development of artificial intelligence (AI) technologies, including affective computing. Affective computing, which focuses on recognizing, interpreting, and ...
Sep 25, 2023
0
11