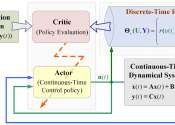
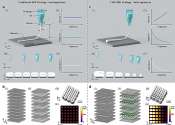
Discrete-time rewards efficiently guide the extraction of continuous-time optimal control policy from system data
The concept of reward is central in reinforcement learning and is also widely used in the natural sciences, engineering, and social sciences. Organisms learn behavior by interacting with their environment and observing the ...
22 hours ago
0
12