'Self-healing' solar cells could become reality
Solar cells of the future could be able to withstand corrosive susceptibility by "self-healing," in a break-through the scientific community has long been pursuing.
Jun 27, 2024
0
47
Electronics & Semiconductors

Solar cells of the future could be able to withstand corrosive susceptibility by "self-healing," in a break-through the scientific community has long been pursuing.
Jun 27, 2024
0
47
Engineering
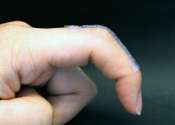
To advance soft robotics, skin-integrated electronics and biomedical devices, researchers at Penn State have developed a 3D-printed material that is soft and stretchable—traits needed for matching the properties of tissues ...
Jun 27, 2024
0
33
Robotics

Amid the unpredictability and occasional chaos of emergency rooms, a robot has the potential to assist health care workers and support clinical teamwork, Cornell and Michigan State University researchers found.
Jun 27, 2024
1
13
Engineering
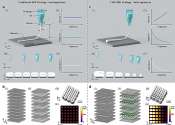
Material extrusion 3D printing technology is widely utilized in biofabrication/bioprinting, tissue engineering, flexible electronics, and soft robotics. However, the fixed printing parameters and constant filament diameter ...
Jun 28, 2024
0
19
Energy & Green Tech

Water electrolysis offers an ideal process for hydrogen production, which could play a key role in the global energy transition that increasingly relies on renewable electricity, but whose current production process is extremely ...
Jul 12, 2024
0
106
Computer Sciences

Researchers at USC have developed a new method to accurately predict wildfire spread. By combining satellite imagery and artificial intelligence, their model offers a potential breakthrough in wildfire management and emergency ...
Jul 22, 2024
0
29
Machine learning & AI
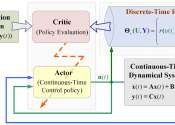
The concept of reward is central in reinforcement learning and is also widely used in the natural sciences, engineering, and social sciences. Organisms learn behavior by interacting with their environment and observing the ...
Jun 28, 2024
0
12
Electronics & Semiconductors

Researchers have developed a novel 3D stretchable electronic strip which is expected to open up a range of new possibilities in wearable electronic textiles.
Jul 3, 2024
0
55
Energy & Green Tech

A research team from the School of Engineering of the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) has shown the existence of surface concavities on individual crystal grains, which are the fundamental building ...
Jul 19, 2024
0
24
Computer Sciences

When it comes to artificial intelligence, appearances can be deceiving. The mystery surrounding the inner workings of large language models (LLMs) stems from their vast size, complex training methods, hard-to-predict behaviors, ...
Jul 11, 2024
0
11
An engine is a mechanical device that produces some form of output from a given input. An engine whose purpose is to produce kinetic energy output from a fuel source is called a prime mover; alternatively, a motor is a device which produces kinetic energy from other forms of energy (such as electricity, a flow of hydraulic fluid or compressed air). A motor car (automobile) has a starter motor and motors to drive pumps (fuel, power steering, etc) – but the power plant that propels the car is called an engine. The term 'motor' was originally used to distinguish the new internal combustion engine -powered vehicles from earlier vehicles powered by a steam engine (as in steam roller and motor roller).
Military engines included siege engines, large catapults, trebuchets and battering rams.
This text uses material from Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY-SA