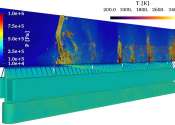
Detonation-based device for novel propulsion applications
Combustors that drive propulsion systems are often volumetric in nature, typically in the form of cylinders, and convert chemical to thermal and mechanical energy through oxidation of fuels. This deflagrating combustion approach ...
Nov 28, 2023
0
50