Self-assembling, highly conductive sensors could improve wearable devices
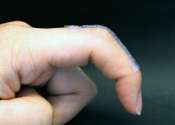
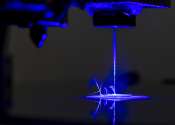
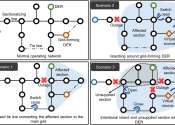
To advance soft robotics, skin-integrated electronics and biomedical devices, researchers at Penn State have developed a 3D-printed material that is soft and stretchable—traits needed for matching the properties of tissues ...
Jun 27, 2024
0
33