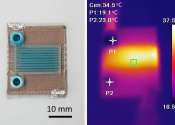
New devices for conveying olfactory stimuli in virtual reality
A team of biomedical and mechanical engineers at City University of Hong Kong, working with a pair of colleagues from Beihang University and one from Shandong University, has developed two versions of a system designed to ...