Is it a bird, a plane? Not superman, but a flapping wing drone
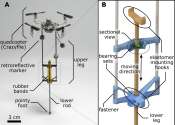
A drone prototype that mimics the aerobatic manoeuvres of one of the world's fastest birds, the swift, is being developed by an international team of engineers in the latest example of biologically inspired flight.
Jul 22, 2020
0
190