Catalytic process with lignin could enable 100% sustainable aviation fuel
An underutilized natural resource could be just what the airline industry needs to curb carbon emissions.
Sep 23, 2022
0
373
Energy & Green Tech

An underutilized natural resource could be just what the airline industry needs to curb carbon emissions.
Sep 23, 2022
0
373
Robotics

A team of engineers at Google's DeepMind Project has demonstrated a robot capable of playing amateur-level table tennis (ping-pong). The team has published a paper on the arXiv preprint server describing how they developed ...
Energy & Green Tech
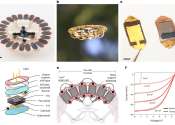
Whether on Earth or in space, autonomous energy is critical in order to keep power systems running independently for extended periods of time, particularly in remote or unpredictable environments.
Apr 24, 2024
0
81
Engineering

Coal is an abundant resource in the United States that has, unfortunately, contributed to climate change through its use as a fossil fuel. As the country transitions to other means of energy production, it will be important ...
Jan 3, 2024
0
74
Engineering

Evaporation is happening all around us all the time, from the sweat cooling our bodies to the dew burning off in the morning sun. But science's understanding of this ubiquitous process may have been missing a piece all this ...
Oct 31, 2023
0
235
Energy & Green Tech

Northwestern University engineers have developed the first computer coding platform that enables kids to build and program sustainable, battery-free, energy-harvesting devices.
Mar 30, 2022
0
32
Hardware

Johns Hopkins electrical and computer engineers are pioneering a new approach to creating neural network chips—neuromorphic accelerators that could power energy-efficient, real-time machine intelligence for next-generation ...
Mar 5, 2024
0
130
Business

Taiwanese chipmaker TSMC agreed Tuesday on a multibillion-dollar deal to build a plant in Germany, part of a push to put Europe at the center of the global semiconductor industry.
Aug 8, 2023
0
45
Security

After remaking their security procedures following the 9/11 attacks to stop airline hijackings, carriers are now faced with rising threats targeting computers and electronic equipment critical to their operations and safety.
Sep 11, 2021
0
48
Energy & Green Tech

Engineers at the University of Illinois Chicago are among a collaborative team that has developed a material that could give fuel cell systems a competitive edge over the battery systems that currently power most electric ...
Mar 31, 2022
1
201
An industry (from Latin industrius, "diligent, industrious") is the manufacturing of a good or service within a category. Although industry is a broad term for any kind of economic production, in economics and urban planning industry is a synonym for the secondary sector, which is a type of economic activity involved in the manufacturing of raw materials into goods and products.
There are four key industrial economic sectors: the primary sector, largely raw material extraction industries such as mining and farming; the secondary sector, involving refining, construction, and manufacturing; the tertiary sector, which deals with services (such as law and medicine) and distribution of manufactured goods; and the quaternary sector, a relatively new type of knowledge industry focusing on technological research, design and development such as computer programming, and biochemistry. A fifth quinary sector has been proposed encompassing nonprofit activities. The economy is also broadly separated into public sector and private sector, with industry generally categorized as private. Industries are also any business or manufacturing.
Industry in the sense of manufacturing became a key sector of production and labour in European and North American countries during the Industrial Revolution, which upset previous mercantile and feudal economies through many successive rapid advances in technology, such as the steel and coal production. It is aided by technological advances, and has continued to develop into new types and sectors to this day. Industrial countries then assumed a capitalist economic policy. Railroads and steam-powered ships began speedily establishing links with previously unreachable world markets, enabling private companies to develop to then-unheard of size and wealth. Following the Industrial Revolution, perhaps a third of the world's economic output is derived from manufacturing industries—more than agriculture's share.
Many developed countries (for example the UK, the U.S., and Canada) and many developing/semi-developed countries (People's Republic of China, India etc.) depend significantly on industry. Industries, the countries they reside in, and the economies of those countries are interlinked in a complex web of interdependence.
This text uses material from Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY-SA