Best hope yet for aluminium-ion batteries
UNSW Sydney's Dr. Dong Jun Kim has led a team of researchers to show rechargeable aluminium-ion batteries are a possibility with a future in renewable energy storage.
Dec 4, 2018
0
159
Energy & Green Tech

UNSW Sydney's Dr. Dong Jun Kim has led a team of researchers to show rechargeable aluminium-ion batteries are a possibility with a future in renewable energy storage.
Dec 4, 2018
0
159
Energy & Green Tech

A future powered by sustainable energy sources could save the world from devastating climate change and reduce energy bills. But renewable energy has an intermittency problem—the sun provides no power at night, while winds ...
Feb 3, 2022
0
57
Electronics & Semiconductors

Haste makes waste, as the saying goes. Such a maxim may be especially true of batteries, thanks to a new study that seeks to identify the reasons that cause the performance of fast charged lithium-ion batteries to degrade ...
Dec 2, 2021
2
226
Energy & Green Tech

What if you could solve two of Earth's biggest problems in one stroke? UC Riverside engineers have developed a way to recycle plastic waste, such as soda or water bottles, into a nanomaterial useful for energy storage.
Aug 12, 2020
1
367
Energy & Green Tech

An international team of researchers are hoping that a new, low-cost battery which holds four times the energy capacity of lithium-ion batteries and is far cheaper to produce will significantly reduce the cost of transitioning ...
Dec 7, 2022
2
181
Energy & Green Tech
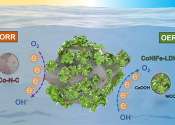
Zinc-air batteries have emerged as a better alternative to lithium in a recent Edith Cowan University (ECU) study into the advancement of sustainable battery systems.
Aug 18, 2023
1
83
Energy & Green Tech

New cathode material for sodium-ion batteries is inspired by earlier work at Argonne that led to the lithium-ion batteries in the Chevy Volt and Bolt. It could help the supply of low-cost and abundant elements for electric ...
Jan 8, 2024
0
38
Energy & Green Tech

Researchers at the University of Illinois at Chicago and at Argonne National Laboratory have designed a new lithium-air battery that works in a natural-air environment and still functioned after a record-breaking 750 charge/discharge ...
Mar 21, 2018
1
570
Energy & Green Tech

Researchers at the University of California, Riverside's Bourns College of Engineering have used waste glass bottles and a low-cost chemical process to create nanosilicon anodes for high-performance lithium-ion batteries. ...
Apr 19, 2017
4
32
Energy & Green Tech

Lithium-ion batteries have become the energy storage method of choice for consumer electronics and military and aerospace systems alike. But potential safety hazards associated with the organic electrolytes that are used ...
Nov 10, 2017
4
895
An ion is an atom or molecule where the total number of electrons is not equal to the total number of protons, giving it a net positive or negative electrical charge.
Since protons are positively charged and electrons are negatively charged, if there are more electrons than protons, the atom or molecule will be negatively charged. This is called an anion (pronounced /ˈænaɪən/; an-eye-on), from the Greek ἀνά (ana), meaning 'up'.
Conversely, if there are more protons than electrons, the atom or molecule will be positively charged. This is called a cation (pronounced /ˈkætaɪən/; cat-eye-on), from the Greek κατά (kata), meaning 'down'.
An ion consisting of a single atom is called a monatomic ion. If it consists of two or more atoms, it is called a polyatomic ion. Polyatomic ions containing oxygen, such as carbonate and sulfate, are called oxyanions.
When writing the chemical formula for an ion, its charge is written as a superscript '+' or '−' following a number indicating the difference between the number of protons and the number of electrons. The number is omitted if it is equal to 1. For example, the sodium cation is written as Na+, the '+' indicating that it has one less electron than it has protons. The sulfate anion is written as SO42−, the '2−' indicating that it has two more electrons than it has protons.
If an ion contains unpaired electrons, it is called a radical ion. Just like neutral radicals, radical ions are very reactive.
This text uses material from Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY-SA