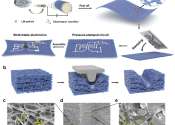
A new method to fabricate stretchable and breathable electronics
In recent years, engineers and material scientists have introduced increasingly flexible electronics that could be used to create new wearable devices, such as smart watches, biosensors and health-monitoring technologies. ...