Study employs image-recognition AI to determine battery composition and conditions
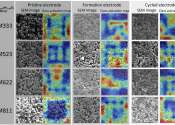
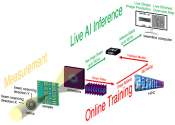
An international collaborative research team has developed an image recognition technology that can accurately determine the elemental composition and the number of charge and discharge cycles of a battery by examining only ...
Jul 2, 2024
0
45