Exploit steals passwords by tapping into keystrokes
Add one more threat to the list of risks you take when you use your phone to conduct business at the local coffee shop.
Internet

Add one more threat to the list of risks you take when you use your phone to conduct business at the local coffee shop.
Telecom
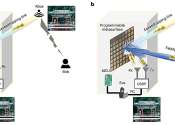
Metasurfaces, artificially engineered surfaces that can manipulate electromagnetic signals in unique ways, have huge potential for several technological applications, including the implementation of sixth generation (6G) ...
Engineering

In recent years, teams of engineers worldwide have been trying to develop acoustic devices based on piezoelectrics (i.e., materials that can produce electricity when mechanical stress is applied to them) integrated with conventional ...
Energy & Green Tech

The world's first solid-state photovoltaics were reported in 1883, and were composed of selenium, which eventually led to the development of the present-day photovoltaics, although the wide bandgap of selenium was limiting ...
Engineering

The next generation of phones and wireless devices will need new antennae to access higher and higher frequency ranges. One way to make antennae that work at tens of gigahertz—the frequencies needed for 5G and higher devices—is ...
Oct 26, 2022
1
333
Electronics & Semiconductors

Wireless sensors can monitor how temperature, humidity or other environmental conditions vary across large swaths of land, such as farms or forests.
Mar 16, 2022
0
36
Electronics & Semiconductors

Emerging 5G wireless systems are designed to support high-bandwidth and low-latency networks connecting everything from autonomous robots to self-driving cars. But these large and complex communication networks could also ...
Nov 23, 2021
0
344
Electronics & Semiconductors

In a move that could one day free the world's countertops from their snarl of charging cords, researchers at the University of Michigan and University of Tokyo have developed a system to safely deliver electricity over the ...
Aug 30, 2021
3
392
Electronics & Semiconductors

Electronic filters are essential to the inner workings of our phones and other wireless devices. They eliminate or enhance specific input signals to achieve the desired output signals. They are essential, but take up space ...
Aug 11, 2020
0
123
Engineering

In the not-too-distant future, flexible electronics will open the door to new products like foldable phones, tablets that can be rolled, paper-thin displays and wearable sensors that monitor health data. Developing these ...
Jun 23, 2020
0
86
Wireless communication is the transfer of information over a distance without the use of electrical conductors or "wires". The distances involved may be short (a few meters as in television remote control) or long (thousands or millions of kilometers for radio communications). When the context is clear, the term is often shortened to "wireless". Wireless communication is generally considered to be a branch of telecommunications.
It encompasses various types of fixed, mobile, and portable two way radios, cellular telephones, personal digital assistants (PDAs), and wireless networking. Other examples of wireless technology include GPS units, garage door openers and or garage doors, wireless computer mice, keyboards and headsets, satellite television and cordless telephones.
This text uses material from Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY-SA