March 16, 2015 feature
Half-millimeter-thick battery could be worn in a wrinkle-smoothing patch
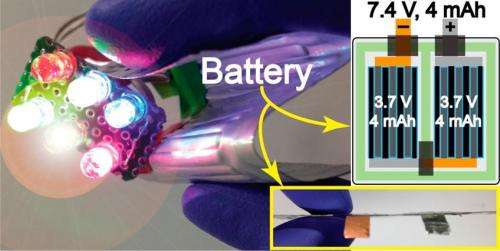
(Phys.org)—As the batteries under development in today's research labs are looking less like large blocks of metal and more like pieces of plastic wrap, their novel applications are coming closer to reality. One of the latest flexible batteries is thinner than a credit card, and could be integrated into various applications such as wrinkle-smoothing patches, smart cards, and watch straps.
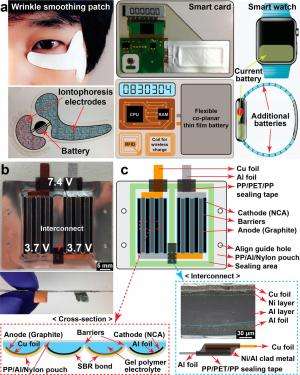
The new 0.5-mm-thick battery achieves its ultra-thinness by its new design. Whereas the electrodes in most existing flexible Li-ion batteries are stacked on top of each other, in the new battery the electrodes are positioned next to each other on the same plane, resulting in a format that is so thin it is essentially two-dimensional.
The researchers, Jang Wook Choi and his group from KAIST in South Korea, say that to their best of their knowledge, this is the first battery designed for bulk flexible applications that uses this so-called "coplanar interdigitated structure." The only other batteries that use the coplanar interdigitated structure so far have been microbatteries designed for limited applications.
Positioning the electrodes side by side not only makes the battery extremely thin, it also offers other performance advantages. Overall, the new battery exhibits a high voltage (7.4 V) that is retained over 5,000 bending cycles.
"The greatest significance of this work is reducing the thickness of the battery while demonstrating robust bendability and cell performance," Choi told Phys.org.
The good performance is made possible by placing the 2-mm-wide electrodes very close together, about 400 µm apart from each other in the current configuration. However, with the electrodes so close, there is a high risk that the battery will short-circuit. To address this problem, the researchers incorporated interelectrode barriers along with a curvy electrode structure. The barriers block direct contact between adjacent electrodes, while the curvy electrode structure ensures that the ends of adjacent electrodes don't come in contact with each other during bending.
The researchers predict that the battery performance can be further improved by decreasing the interelectrode distance. In the current study, the scientists used molds to fabricate the electrodes, but they expect that printing techniques could produce more precise, detailed patterns, and at higher speeds.
"Future plans include developing a process for scalable production, such as printing techniques," Choi said.
One of the battery's primary target applications is medical and cosmetic patches. These devices work by iontophoresis, in which ions driven by an electric field deliver medicine through the skin. Another application, smart cards, can store information for a variety of purposes, such as financial, personal, and medical information. The batteries may also be integrated into watch straps where they can serve as supplementary power sources to recharge personal electronic devices such as phones.
Adding to its practical use, the researchers also demonstrated that the battery can be wirelessly recharged as well as recharged by an integrated solar cell. To demonstrate wireless charging, the researchers connected the battery to a receiving coil that receives electromagnetic energy from a transmitting coil located about 1 cm away. The researchers plan to further elaborate on this possibility in future work. To demonstrate solar charging, they connected the battery to a commercially available flexible solar cell, which could fully charge the battery after several hours' exposure to sunlight.
More information: Joo-Seong Kim, et al. "A Half Millimeter Thick Coplanar Flexible Battery with Wireless Recharging Capability." Nano Letters. DOI: 10.1021/nl5045814
© 2015 Phys.org