Novel vision-based algorithm to track position of spacecraft in real time
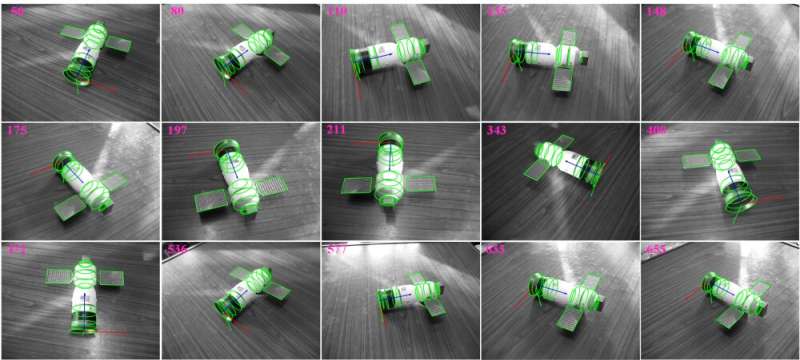
Guidance, navigation, and control technologies on spacecraft require accurate tracking of the relative six-degree-of-freedom (6-DOF) pose of the spacecraft at close range during space maneuvers such as debris removal, landing, rendezvous and docking.
Computer vision techniques have recently become increasingly crucial in 6-DOF pose tracking due to their low energy consumption, rapidness, long work range, and low cost.
However, traditional vision-based pose tracking methods suffer from relatively low accuracy, long runtime and incapability of determining the position of spacecraft with multi-rigid-body structures.
Researchers from the Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and their collaborators from Beihang University have developed a novel vision-based algorithm to track the 6-DOF position of a multi-rigid-body spacecraft in real time. The study was published in IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems.
On a general spacecraft, there exists plenty of geometric primitives (GPs) such as line segments, circles, spheres, cones, cylinders, developable surfaces, etc. The proposed algorithm tracks the 6-DOF pose of spacecraft by geometrically fitting the GPs on the spacecraft with the Generalized Expectation-Maximization, M-estimation and Extended Kalman Filter.
Eventually, this algorithm could provide the maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) for spacecraft positioning and outperform other modern position tracking methods in terms of accuracy and rapidness.
Extensive synthetic and real experiments have verified that the proposed algorithm could fulfill the position tracking of spacecraft with about 33.33Hz, with satisfactory robustness to random noise, background clutter and dramatic illumination changes in the space environment.
More information: Chang Liu et al. Real-time Vision-based Pose Tracking of Spacecraft in Close Range Using Geometric Curve Fitting, IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems (2020). DOI: 10.1109/TAES.2020.2996074