Printing perovskite solar cells
To reach the target of carbon neutral, a transition from fossil energy to renewable energy generation is indispensable. Photovoltaic technology is considered as one of the most prominent sources of renewable energy. For decades, about 90% of global solar cell market has been dominated by silicon solar cells. Although the price of silicon solar panels decreases year by year, it is a big challenge to significantly reduce its manufacturing cost further. Hence, next-generation photovoltaic technologies are in urgent need of new materials and novel techniques. Recently, metal halide perovskite solar cells (PSCs) have attracted extensive attention from both academia and industry, due to their excellent photoelectric conversion efficiency and great commercial potential.
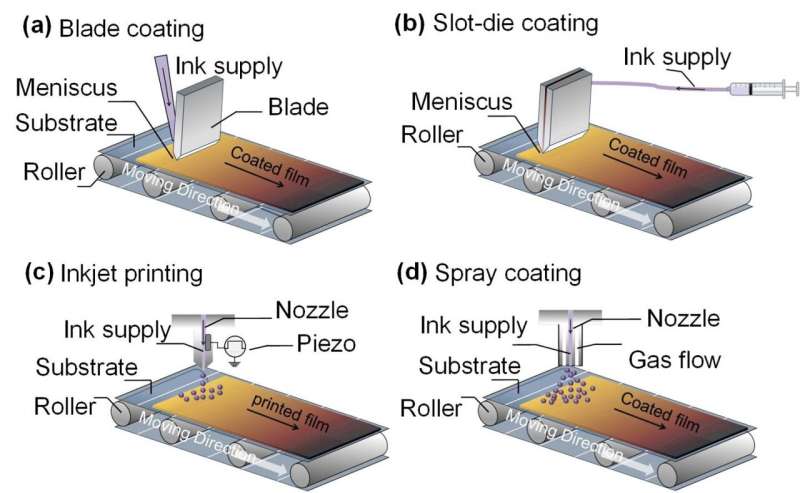
Metal halide perovskite materials can be easily synthesized in solution at low-temperature and deposited into thin-film through a variety of printing method. Recently, many reviews have been published on the topic of perovskite film deposition techniques/mechanisms, such as solvent engineering and additives-engineering, whereas discussions about ink engineering for printing high-quality perovskite films as well as other function layers are few.
In this article, the authors provide a systematical overview of applicable printing technologies that can be possibly used for scaling-up PSCs. The authors consider the ink engineering is the key issue to achieve high quality thin films for efficient solar cells. Therefore, they mainly focus on the perspective of perovskite precursor ink formula and additives on controlling the film formation process. They analyze the potential physical and chemical mechanisms of the nucleation and crystallization process during the printing. For the additives in the printing of PSCs, the authors discuss the effect of additives for the film formation process, the microstructure and defect population.
Moreover, they also present the technical feasibility of printing the other layers besides perovskite layers, including hole transporting layers (HTL) and electron transporting layers (ETL), which might enable a rapid and mass production of PSCs. Finally, they introduce the recent progress of roll-to-roll (R2R) printing and the stability issues of perovskite modules, and give a prospect of mass production of perovskite solar modules in the near future.
More information: Yulong Wang et al, Printing strategies for scaling-up perovskite solar cells, National Science Review (2021). DOI: 10.1093/nsr/nwab075