August 16, 2023 report
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
A supramolecular organo-ionic electrolyte that can be liquidated for recycling
A team of molecular foundry and energy storage engineers at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory has developed an electrolyte material for use in solid state batteries that allows for reuse of cathodes at up to 90% capacity. In their paper published in the journal Science Advances, the group describes their electrolyte, how it was made, and how well it has done during testing.
Most electric vehicles sold in the world today are powered using lithium-ion batteries—a type that has been designed with a high power-to-weight ratio. Such batteries have been proven to be useable in such applications but they suffer from two major drawbacks—they are heavy and they are difficult to recycle. In this new effort, the team in Berkeley sought to improve on the latter problem by developing a new kind of battery based on a different kind of electrolyte.
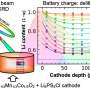
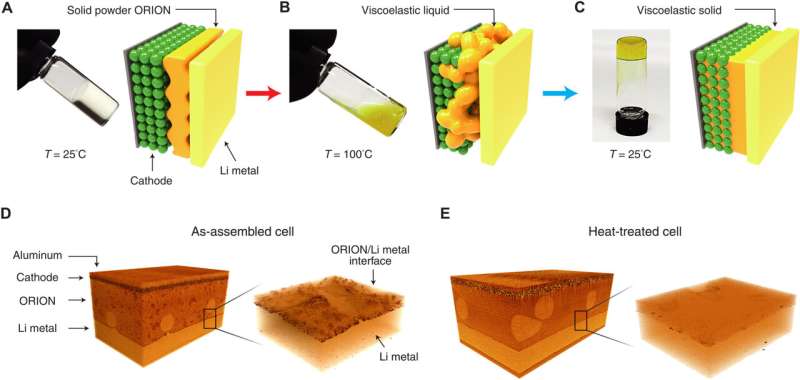
Lithium-ion batteries, as their name implies, are based on lithium salt electrolytes. In this new effort, the team started with the same salt when making their new electrolyte, but added organic-based zwitterionic polymers to change its properties. They created a battery by sandwiching their new electrolyte between an anode made of lithium metal and cathodes made of different materials—lithium iron, phosphate, nickel, cobalt and manganese.
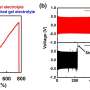
The resulting battery, the researchers suggest, regardless of the type of cathode used, is much more recyclable than current batteries because the polymer in the electrolyte allows the entire electrolyte to melt at 100° C. Once the electrolyte is melted, the battery can be very easily disassembled, allowing for each of its parts to be recycled separately. The team notes that before melting, the electrolyte is highly conductive, viscoelastic, and solid at typical operating temperatures.
Testing of the battery showed it to have high conductivity at temperatures up to 45° C. The team also found that the cathode was able to maintain 90% of its original capacity after the battery was disassembled, allowing for easy recycling.
More testing will need to be done, but the research team is confident that the new electrolyte will stand up to scrutiny, paving the way for future EVs that have more environmentally friendly batteries.
More information: Jiwoong Bae et al, Closed-loop cathode recycling in solid-state batteries enabled by supramolecular electrolytes, Science Advances (2023). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adh9020
© 2023 Science X Network