This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Researchers develop a PEMFC battery configuration that is 10% more efficient
A team at the Department of Energy Engineering of the University of Seville have carried out experimental research focusing on the dynamic behavior of a proton-exchange membrane fuel cell battery (PEMFC) for different reagent input/output configurations. Their results, published in the journal Energy, show that the most effective configuration can obtain up to 10% more than other options.
Currently, PEMFCs are commercially available not only for stationary uses but also for mobility applications as an alternative to internal combustion engines since they are based on clean technology with zero emissions, have a relatively simple design and are more efficient. Another factor in their favor is that PEMFCs have several advantages over electric batteries—they weigh less, and are smaller, cheaper and take less time to recharge.
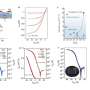
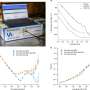
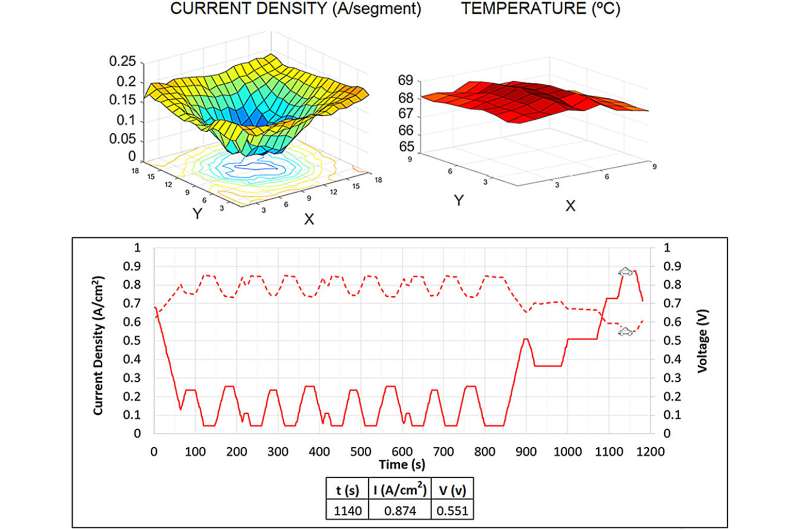
PEMFCs for the transport sector need to be specially designed and durable, and perform stably and reliably under variable cyclical loads. To this end, experimental testing of dynamic load cycles (DLC) and current density mapping (CDM) of local currents and temperatures were carried out, subjecting the fuel cell to cycles of repetitive loads to measure the effect to measure the effect of different periods of acceleration, braking and constant speed on the density fields of current and temperature inside the fuel cell.
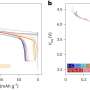
The results showed that the reverse hydrogen flow configuration had the lowest performance, with maximum differences in energy terms during the cycle of up to 10% when comparing the best configuration (reverse hydrogen flow) to the worst. Current density mapping showed an inverted bell curve distribution with higher current density values in the outer areas of the bipolar plate and lower values in the center, and very uniform temperature distributions in all the configurations.
More information: Christian Suárez et al, Experimental dynamic load cycling and current density measurements of different inlet/outlet configurations of a parallel-serpentine PEMFC, Energy (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.energy.2023.128455