This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Low-power vertical neurotransistors emulate dendritic computing of neurons
An important avenue for information processing, especially at the edge of limited resources, is to develop neuromorphic devices with functions similar to biological neural networks.
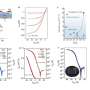
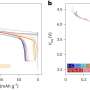
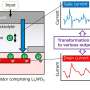
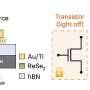
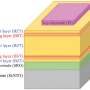
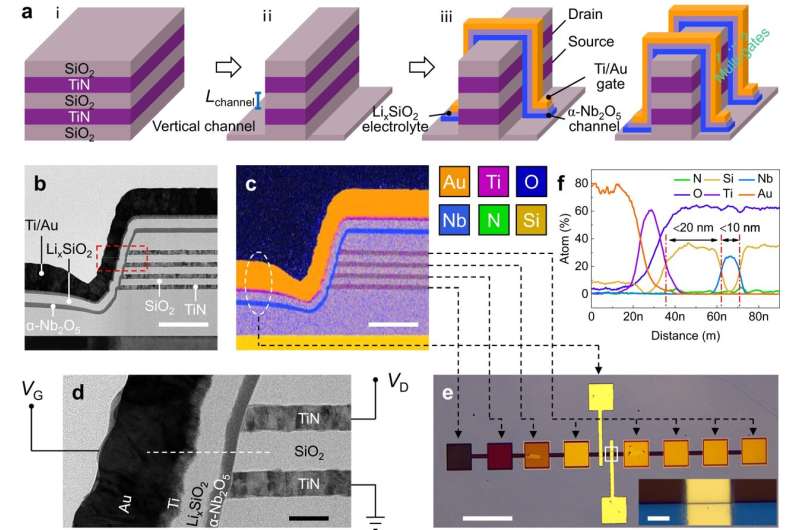
In a study published in Nature Communications, Prof. Shang Dashan's group at the Institute of Microelectronics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (IMECAS) has developed a vertical dual-gate electrolyte-gated transistor, named a neurotransistor, with a 30 nm channel length, short-term memory characteristic and stackability for 3D integration. The read power and energy reach ~3.16 fW and ~30 fJ, which is close to a biological level.
The electrolyte-gated transistor uses electrolyte materials with mobile ions (such as H+, Li+, O2-) as gate dielectric. The migration of ions driven by the gate voltage toward the channel produces multi-level short-term memory effects of the channel conductance, which is very similar to the dendritic behavior of neurons.
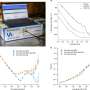
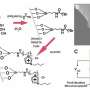
The researchers used the short-term memory characteristics of the neurotransistors to realize the dendrite computing function in biological neurons, such as dendrite integration and coincidence detection. The dendrite computing ability is extended to the recognition of sound azimuth and distance by integrating neurotransistors into a bionic sound localization neural network.
This work not only demonstrates the potential of neurotransistors as building blocks to emulate the advanced functions of biological neural networks, but also provides a novel approach for the development of edge-oriented, high-density, low-energy neuromorphic computing hardware systems from a device level.
More information: Han Xu et al, A low-power vertical dual-gate neurotransistor with short-term memory for high energy-efficient neuromorphic computing, Nature Communications (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-42172-y