This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
New approach helps to improve classification accuracy of remote sensing image

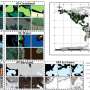
Land use/land cover (LULC) is a major shaper of the ecological environment. Using remote sensing technology to dynamically monitor LULC and quantitatively extract LULC change information is an important study for coping with global climate change and maintaining the energy balance of the Earth system.
Deep learning has been shown to be effective in extracting LULC from remote sensing images. In recent years, the integration of multiple deep learning models has become an effective method to improve the classification accuracy of remote sensing images, but these integration methods ignore the internal correlation between pixels, resulting in high training time cost and limited accuracy improvement.
A research team led by Prof. Huang Chunlin from the Northwest Institute of Eco-Environment and Resources of the Chinese Academy of Sciences conducted a study on the internal relationship of pixels and its use for remote sensing image classification.
The study was published in ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing.
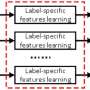
The researchers found that using the association information between pixels to build different assemblies can eliminate the dependence on multiple models in the process of integrated classification.
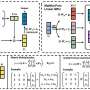
They proposed a doublets-based ensemble classification framework (DBECF), which eliminates the need for multiple classifiers in order to improve the classification accuracy of remote sensing images.
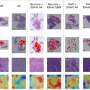
The DBECF can effectively improve the classification accuracy of different types of remote sensing images, and has obvious advantages in accuracy and efficiency compared with the existing single pixel-based integrated classification model.
Compared with the traditional single instance-based classification, DBECF can achieve diverse classification results through different instance combinations, which presents conditions and potentials for improving accuracy and efficiency through ensemble strategies.
In addition, DBECF overcomes the time-consuming drawbacks of the current integrated classification model, provides a new perspective for the combination of deep learning and ensemble learning, and has important theoretical reference and practical value for extracting high-quality LULC to support large-scale and long-time series geoscience research.
More information: Peng Dou et al, Remote sensing image classification using an ensemble framework without multiple classifiers, ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2023.12.012