Lithium-ion batteries are no longer the gold standard in battery tech, researchers say
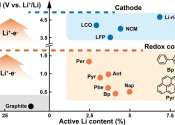
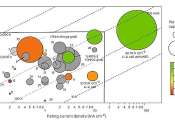
The use of lithium metal as the anode for batteries is one of the smarter options with better energy density than other materials. However, the interface between the electrode and electrolyte has quite a few issues that can ...
Nov 16, 2023
0
30