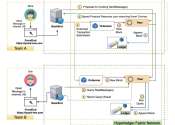
A decentralized, blockchain-based messaging network for safer communications
Data and security breaches are becoming increasingly common, highlighting the vulnerabilities of existing messaging and communications platforms. Devising computational tools and systems that better protect sensitive data ...