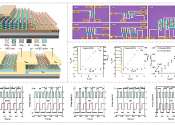
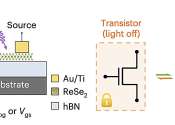
Study demonstrates the non-volatile electrical control of a 2D magnetic insulator using a thin ferroelectric polymer
Two-dimensional (2D) magnetic insulators, which are electrically insulating materials with long-range magnetic order, could be used to fabricate compact magneto-electric or magneto-optical devices. Efficiently and reliably ...