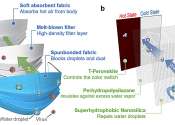
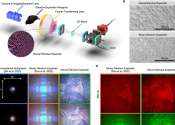
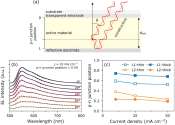
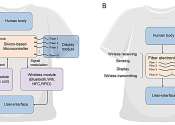
Mask-inspired perovskite smart windows enhance weather resistance and energy efficiency
Thermochromic perovskite is a new color switch material used in energy-saving smart windows. Despite its potential for energy savings, thermochromic perovskite suffers from poor weather resistance, susceptibility to water ...
18 hours ago
0
1