New aluminum radical battery promises more sustainable power
Scientists in Australia and China are hoping to make the world's first safe and efficient non-toxic aqueous aluminum radical battery.
Jul 4, 2023
0
110
Energy & Green Tech

Scientists in Australia and China are hoping to make the world's first safe and efficient non-toxic aqueous aluminum radical battery.
Jul 4, 2023
0
110
Robotics
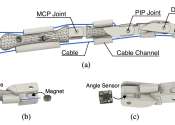
In recent years, roboticists have developed increasingly sophisticated robotic systems designed to mimic both the structure and function of the human body. This work includes robotic hands, grippers that allow robots to grasp ...
Robotics

An international team led by researchers at the RIKEN Cluster for Pioneering Research (CPR) has engineered a system for creating remote controlled cyborg cockroaches, equipped with a tiny wireless control module that is powered ...
Sep 5, 2022
2
749
Engineering

Three-dimensional (3D) printing has become increasingly advanced over the past few years and has been successfully used to create countless items, including toys, furniture and electronic components. As 3D printing equipment ...
Energy & Green Tech

Physicists in the U.S. jumped a major hurdle standing in the way of the commercialization of solar cells created with halide perovskites as a lower-cost, higher-efficiency replacement for silicon when generating electricity ...
Feb 16, 2023
1
157
Robotics

Utilizing soft, flexible materials such as cloth, paper, and silicone, soft robotic grippers act like a robot's hand to perform functions such as safely grasping and releasing objects. Unlike conventional rigid material grippers, ...
Oct 6, 2023
0
92
Engineering

A team of EPFL engineers has developed a 3D-printing method that uses light to make objects out of opaque resin in a matter of seconds. Their breakthrough could have promising applications in the biomedical industry, such ...
May 23, 2022
0
262
Energy & Green Tech

University of Texas at Austin researchers have created a new sodium-based battery material that is highly stable, capable of recharging as quickly as a traditional lithium-ion battery and able to pave the way toward delivering ...
Dec 6, 2021
3
3856
Energy & Green Tech

Resistance to adoption of solar panels as an economical and efficient replacement for fossil fuels is based on inaccurate information being spread by foes of renewable energy.
Energy & Green Tech

Production of natural rubber has claimed over 4 million hectares of forest in south-east Asia since 1993 according to a recent study. This destruction of tropical forest for rubber plantations is thought to be 2 to 3 times ...
Jan 12, 2024
0
34
Material is synonymous with Substance, and is anything made of matter - hydrogen, air and water are all examples of materials. Sometimes the term Material is used more narrowly to refer to substances or components with certain physical properties which are used as inputs to production or manufacturing. In this sense, materials are the pieces required to make something else, from buildings and art to stars and computers.
A material can be anything: a finished product in its own right or an unprocessed raw material. Raw materials are first extracted or harvested from the earth and divided into a form that can be easily transported and stored, then processed to produce semi-finished materials. These can be input into a new cycle of production and finishing processes to create finished materials, ready for distribution, construction, and consumption.
An example of a raw material is cotton, which is harvested from plants, and can then be processed into thread (also considered a raw material), which can then be woven into cloth, a semi-finished material. Cutting and sewing the fabric turns it into a garment, which is a finished material. Steelmaking is another example—raw materials in the form of ore are mined, refined and processed into steel, a semi-finished material. Steel is then used as an input in many other industries to make finished products.
This text uses material from Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY-SA