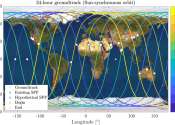
Orbital angular momentum-mediated machine learning for high-accuracy mode-feature encoding
As a derivative product of artificial neural networks, ChatGPT became extremely popular in 2023, breaking the shortest time record for technology product users to exceed 100 million. It is a large-scale language model based ...
Feb 20, 2024
0
1