German solar industry looks to rise again
A decade after a wave of bankruptcies all but wiped out the German solar industry, the sector is looking to reestablish itself in the face of stiff competition from abroad.
Oct 22, 2023
0
33
Energy & Green Tech

A decade after a wave of bankruptcies all but wiped out the German solar industry, the sector is looking to reestablish itself in the face of stiff competition from abroad.
Oct 22, 2023
0
33
Electronics & Semiconductors

Materials scientists at Kiel University and the Fraunhofer Institute for Silicon Technology in Itzehoe (ISIT) have cleared another hurdle in the development and structuring of new materials for next-generation semiconductor ...
Oct 16, 2023
0
106
Internet

Since Elon Musk hollowed out Twitter's staffing, pushed services behind a paywall and renamed it X, many users have been thrashing around for an alternative social media platform.
Oct 11, 2023
0
1
Business

The trial of Sam Bankman-Fried, former CEO of one of cryptocurrency's biggest exchanges, began Tuesday with a jury set to determine if he committed massive fraud by stealing billions of dollars from clients.
Oct 3, 2023
0
4
Business

The artificial intelligence revolution is fully underway, but soaring demand for its most crucial component has startups scratching their heads on how they can deliver on AI's promise.
Sep 28, 2023
0
1
Consumer & Gadgets

Meta chief Mark Zuckerberg on Wednesday said the tech giant is putting artificial intelligence into digital assistants and smart glasses as it seeks to gain lost ground in the AI race.
Sep 28, 2023
0
26
Engineering
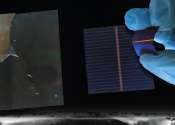
Solar power has become indispensable in our global pursuit of clean energy and sustainability. Today, about 95% of solar cells are made using crystalline silicon (c-Si). Most commercial designs employ a c-Si photoactive layer ...
Sep 27, 2023
0
65
Business

Cisco is buying the cybersecurity firm Splunk in a $28 billion deal as it bolsters its defenses against potential security threats that may be heightened by the widening use of artificial intelligence.
Sep 21, 2023
0
1
Energy & Green Tech
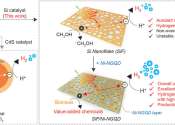
A team of researchers, led by Professor Jungki Ryu in the School of Energy and Chemical Engineering at UNIST and Professor Soojin Park from Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH), have achieved a significant ...
Sep 20, 2023
0
51
Engineering

From smartphones to electric cars, lithium ion batteries have changed the way we power our lives. And in the push towards net zero carbon emissions globally, they will be a vital part of decarbonizing transport networks and ...
Sep 19, 2023
0
21
Silicon (pronounced /ˈsɪlɨkən/ or /ˈsɪlɨkɒn/, Latin: silicium) is the most common metalloid. It is a chemical element, which has the symbol Si and atomic number 14. The atomic mass is 28.0855. A tetravalent metalloid, silicon is less reactive than its chemical analog carbon. As the eighth most common element in the universe by mass, silicon very rarely occurs as the pure free element in nature, but is more widely distributed in dusts, planetoids and planets as various forms of silicon dioxide (silica) or silicates. On Earth, silicon is the second most abundant element (after oxygen) in the crust, making up 25.7% of the crust by mass.
Silicon has many industrial uses. It is the principal component of most semiconductor devices, most importantly integrated circuits or microchips. Silicon is widely used in semiconductors because it remains a semiconductor at higher temperatures than the semiconductor germanium and because its native oxide is easily grown in a furnace and forms a better semiconductor/dielectric interface than any other material.
In the form of silica and silicates, silicon forms useful glasses, cements, and ceramics. It is also a constituent of silicones, a class-name for various synthetic plastic substances made of silicon, oxygen, carbon and hydrogen, often confused with silicon itself.
Silicon is an essential element in biology, although only tiny traces of it appear to be required by animals. It is much more important to the metabolism of plants, particularly many grasses, and silicic acid (a type of silica) forms the basis of the striking array of protective shells of the microscopic diatoms.
This text uses material from Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY-SA