'Deforming' solar cells could be clue to improved efficiency
Solar cells and light sensing technologies could be made more efficient by taking advantage of an unusual property due to deformations and defects in their structures.
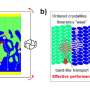
Researchers from the University of Warwick's Department of Physics have found that the strain gradient (i.e. inhomogenous strain) in the solar cells, through physical force or induced during the fabrication process, can prevent photo-excited carriers from recombining, leading to an enhanced solar energy conversion efficiency. The results of their experiments have been published in Nature Communications.
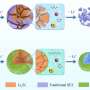
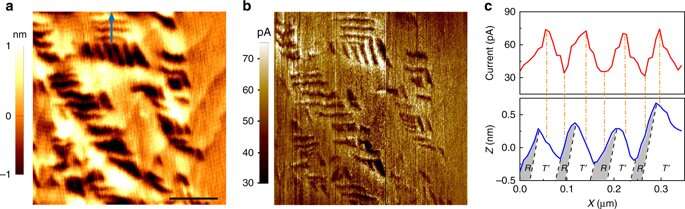
The team of scientists used an epitaxial thin film of BiFeO3 grown on LaAlO3 substrate to determine the impact of inhomogenous deformation on the film's ability to convert light into electricity by examining how its strain gradient affects its ability to separate photo-excited carriers.
Most commercial solar cells are formed of two layers creating at their boundary a junction between two kinds of semiconductors, p-type with positive charge carriers (electron vacancies) and n-type with negative charge carriers (electrons). When light is absorbed, the junction of the two semiconductors sustains an internal field splitting the photo-excited carriers in opposite directions, generating a current and voltage across the junction. Without such junctions the energy cannot be harvested and the photo-excited carriers will simply quickly recombine eliminating any electrical charge.
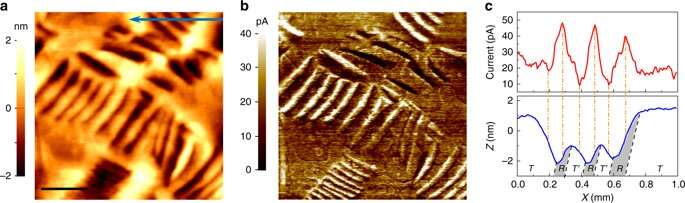
They found that the strain gradient can help prevent recombination by separating the light-excited electron-holes, enhancing the conversion efficiency of the solar cells. The BiFeO3/LaAlO3 film also exhibited some interesting photoelectric effects, such as persistent photoconductivity (improved electrical conductivity). It has potential applications in UV light sensors, actuators and transducers.
Dr. Mingmin Yang from the University of Warwick said: "This work demonstrated the critical role of the strain gradient in mediating local photoelectric properties, which is largely overlooked previously. By engineering photoelectric technologies to take advantage of strain gradient, we may potentially increase the conversion efficiency of solar cells and enhance the sensitivity of light sensors.
"Another factor to consider is the grain boundaries in polycrystalline solar cells. Generally, defects accumulate at the grain boundaries, which would induce photo-carrier recombination, limiting the efficiency. However, in some polycrystalline solar cells, such as CdTe solar cells, the grain boundaries would promote the collection of photo-carriers, where the giant strain gradient might play an important role. Therefore, we need to pay attention to the local strain gradient when we study the structure-properties relations in solar cells and light sensor materials."
Previously, the effect of this strain on efficiency was thought to be negligible. With the increasing miniaturisation of technologies, the effect of strain gradient becomes magnified at smaller sizes. So in reducing the size of a device using one of these films, the magnitude of strain gradient increases dramatically.
Dr. Yang adds: "The strain gradient induced effect, such as flexo-photovoltaic effect, ionic migration, etc, would be increasingly important at low dimensions."
More information: Ming-Min Yang et al. Strain-gradient mediated local conduction in strained bismuth ferrite films, Nature Communications (2019). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-10664-5