3-D hand pose estimation using a wrist-worn camera
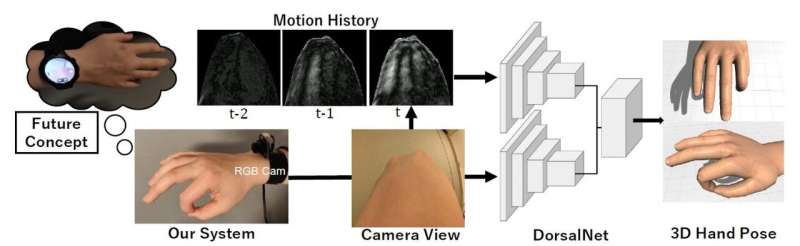
Researchers at Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech) working in collaboration with colleagues at Carnegie Mellon University, the University of St Andrews and the University of New South Wales have developed a wrist-worn device for 3-D hand pose estimation. The system consists of a camera that captures images of the back of the hand, and is supported by a neural network called DorsalNet which can accurately recognize dynamic gestures.
Being able to track hand gestures is of crucial importance in advancing augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) devices that are already beginning to be much in demand in the medical, sports and entertainment sectors. To date, these devices have involved using bulky data gloves which tend to hinder natural movement or controllers with a limited range of sensing.
Now, a research team led by Hideki Koike at Tokyo Tech has devised a camera-based wrist-worn 3-D hand pose recognition system which could in future be on par with a smartwatch. Their system can importantly allow capture of hand motions in mobile settings.
"This work is the first vision-based real-time 3-D hand pose estimator using visual features from the dorsal hand region," the researchers say. The system consists of a camera supported by a neural network named DorsalNet which can accurately estimate 3-D hand poses by detecting changes in the back of the hand.
The researchers confirmed that their system outperforms previous work with an average of 20% higher accuracy in recognizing dynamic gestures, and achieves a 75% accuracy of detecting eleven different grasp types.
The work could advance the development of controllers that support bare-hand interaction. In preliminary tests, the researchers demonstrated that it would be possible to use their system for smart devices control, for example, changing the time on a smartwatch simply by changing finger angle. They also showed it would be possible to use the system as a virtual mouse or keyboard, for example by rotating the wrist to control the position of the pointer and using a simple 8-key keyboard for typing input.
They point out that further improvements to the system such as using a camera with a higher frame rate to capture fast wrist movement and being able to deal with more diverse lighting conditions will be needed for real world use.
More information:
Erwin Wu et al. Back-Hand-Pose: 3D Hand Pose Estimation for a Wrist-worn Camera via Dorsum Deformation Network.
Conference : The Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology 2020. uist.acm.org/uist2020/


















