Seeking stability to support sustainable outdoor solar cells
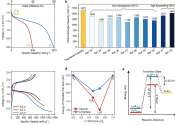
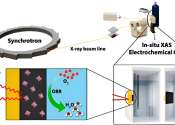
The molecular structure of organic semiconductors is key to the outdoor stability of organic solar cells. Molecular-level insight into one family of organic solar cell materials, known as Y-series nonfullerene acceptors (Y-NFAs), ...
Nov 6, 2023
0
4