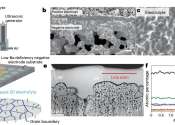
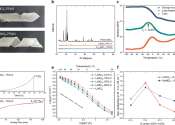
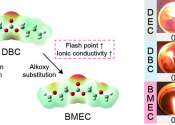
In chemistry, an electrolyte is any substance containing free ions that make the substance electrically conductive. The most typical electrolyte is an ionic solution, but molten electrolytes and solid electrolytes are also possible.
Commonly, electrolytes are solutions of acids, bases or salts. Furthermore, some gases may act as electrolytes under conditions of high temperature or low pressure. Electrolyte solutions can also result from the dissolution of some biological (e.g., DNA, polypeptides) and synthetic polymers (e.g., polystyrene sulfonate), termed polyelectrolytes, which contain charged functional groups.
Electrolyte solutions are normally formed when a salt is placed into a solvent such as water and the individual components dissociate due to the thermodynamic interactions between solvent and solute molecules, in a process called solvation. For example, when table salt, NaCl, is placed in water, the salt (a solid) dissolves into its component ions, according to the dissociation reaction
It is also possible for substances to react with water producing ions, e.g., carbon dioxide gas dissolves in water to produce a solution which contains hydronium, carbonate, and hydrogen carbonate ions.
Note that molten salts can be electrolytes as well. For instance, when sodium chloride is molten, the liquid conducts electricity.
An electrolyte in a solution may be described as concentrated if it has a high concentration of ions, or dilute if it has a low concentration. If a high proportion of the solute dissociates to form free ions, the electrolyte is strong; if most of the solute does not dissociate, the electrolyte is weak. The properties of electrolytes may be exploited using electrolysis to extract constituent elements and compounds contained within the solution.