This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
proofread
Large sequence models for sequential decision-making
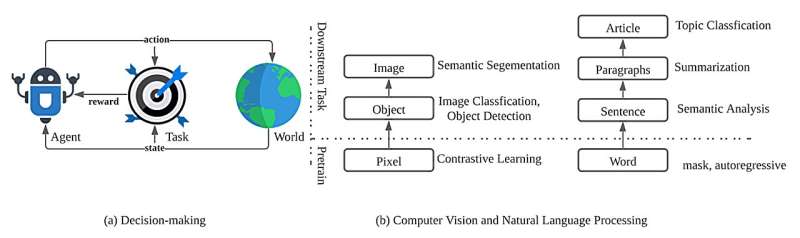
Transformer architectures have facilitated the development of large-scale and general-purpose sequence models for prediction tasks in natural language processing and computer vision, for example, GPT-3 and Swin Transformer.
Although originally designed for prediction problems, it is natural to inquire about their suitability in another important field, sequential decision-making and reinforcement learning problems, which are typically beset by long-standing issues involving sample efficiency, credit assignment, and partial observability, etc.
In recent years, sequence models, especially the Transformer, have attracted increasing interest in the RL communities, spawning numerous approaches with notable effectiveness and generalizability.
To inspire more investigation into this trending topic and empower more real-world applications, e.g., robotics, automatic vehicles, and the automated industry, a research team led by Muning Wen published their survey in Frontiers of Computer Science.
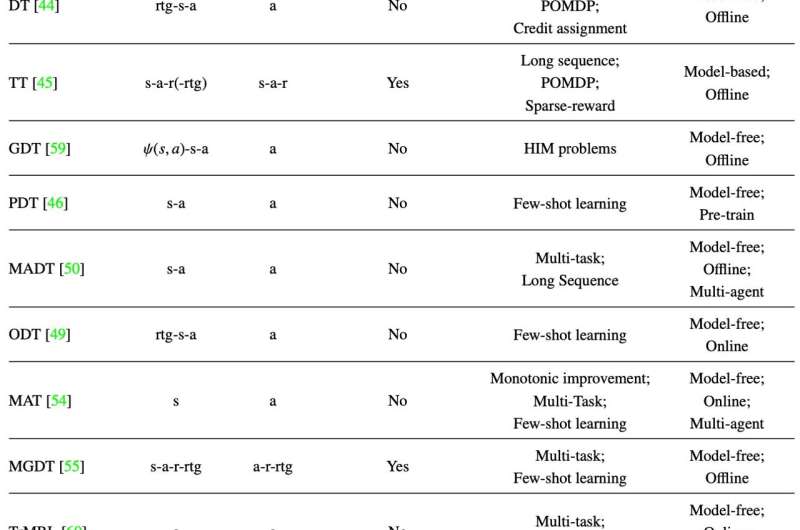
The survey presents a comprehensive overview of recent works aimed at solving sequential decision-making tasks with sequence models such as the Transformer, by discussing the connection between sequential decision-making and sequence modeling, and categorizing them based on the way they utilize the Transformer.
These works suggest the potential for constructing a large decision model for general purposes, that is, a large sequence model that can harness a vast number of parameters to perform hundreds or more sequential decision-making tasks, analogous to the way in which large sequence models have been leveraged for NLP and CV.
To examine the development of the Transformer in the field of sequential decision-making, the authors summarized recent works that convert the reinforcement learning problem into sequential form, to leverage sequence models for specific reinforcement learning settings.
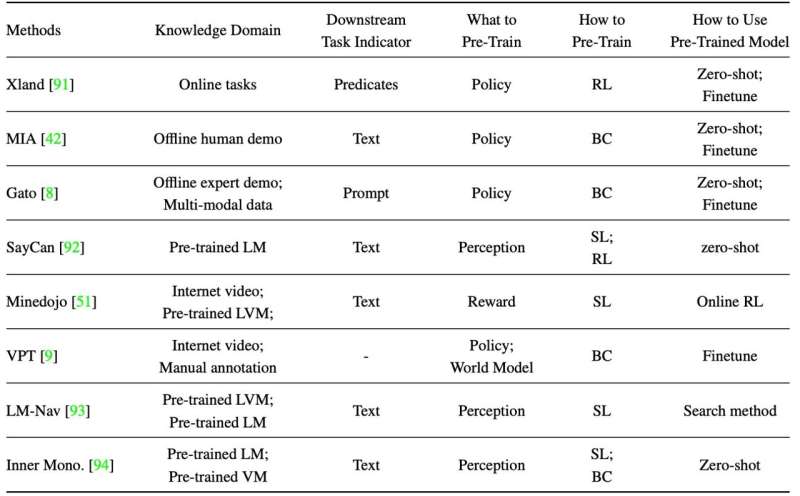
The authors' summary methods leverage diverse data to pre-train a large-scale sequence model for various downstream sequential decision-making tasks, inspired by the tremendous success of NLP and CV.
The team puts forth various potential avenues for future research to improve the effectiveness of large sequence models for sequential decision-making, encompassing theoretical foundations, network architectures, algorithms, and efficient training systems. They hope this survey could inspire more investigation into this trending topic.
More information: Muning Wen et al, Large sequence models for sequential decision-making: a survey, Frontiers of Computer Science (2023). DOI: 10.1007/s11704-023-2689-5